Applications 4: Diferență între versiuni
(Pagină nouă: == Exercise 1 == Make a 7-segment display transcoder using a '''case''' block that displays values from 0 to 9. The input of the module will be called '''value''' and the ou...) |
|||
| Linia 5: | Linia 5: | ||
[[Fișier: segment.png]] | [[Fișier: segment.png]] | ||
The output bits would control the segments of a digit display, one bit for each segment. The segment is | The output bits would control the segments of a digit display, one bit for each segment. The segment is lit when the corresponding bit is '''0''', otherwise it is off (negative logic). | ||
[[Fișier: digits.png]] | [[Fișier: digits.png]] | ||
The simplest implementation is a ROM | The simplest implementation is a ROM | ||
Test the | Test the transcoder by connecting its 4 bit input to SW[3], SW[2], SW[1] and SW[0], and displaying the output on a 7-segment display, the right digit (Digit0) of DE1-SOC display. | ||
'''Coding style:''' | '''Coding style:''' | ||
* '''case''' statements should always include the '''default''' case. | * '''case''' statements should always include the '''default''' case. | ||
== Exercise 2 == | |||
Implement a 3 bit adder whose result is displayed as a hexadecimal digit. | |||
[[Fișier: app4_adder.png]] | |||
The result of the 3 bit addition is in the range [0, ... ,14] and it may be written in the hexadecimal base using only one digit. | |||
The transcoder must be extended to show hexadecimal digits greater than 9. Use the most common 7-segment symbols for them: | |||
[[Fișier: letters.png]] | |||
== Exercise 3 == | |||
Implement a 3 x 3 bits multiplier, with the result shown in decimal base as a 2 digits number. | |||
[[Fișier: app4_multiplier.png]] | |||
This project comprises a top module with 4 blocks. The first block, ''multiplier'', takes in two 3 bit numbers, ''a'' and ''b'', and delivers the result of their multiplication in binary format. The input operands and the result are treated as unsigned integers (natural numbers). | |||
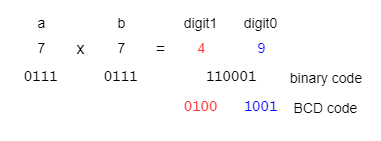
The next block, ''BCD converter'', converts the result from the binary format to the decimal. The decimal digits are coded in binary, therefore a multidigit number is coded | |||
in the so called BCD format (Binary-coded decimal), where each decimal digit is represented as a 4 bit number. | |||
[[Fișier: app4_bcd.png]] | |||
Versiunea de la data 10 martie 2019 22:39
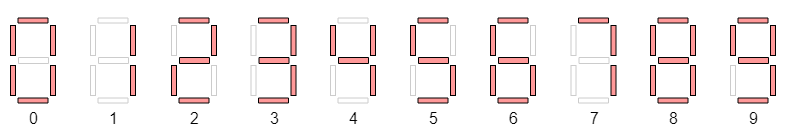
Exercise 1
Make a 7-segment display transcoder using a case block that displays values from 0 to 9. The input of the module will be called value and the output seg.
The output bits would control the segments of a digit display, one bit for each segment. The segment is lit when the corresponding bit is 0, otherwise it is off (negative logic).
The simplest implementation is a ROM Test the transcoder by connecting its 4 bit input to SW[3], SW[2], SW[1] and SW[0], and displaying the output on a 7-segment display, the right digit (Digit0) of DE1-SOC display.
Coding style:
- case statements should always include the default case.
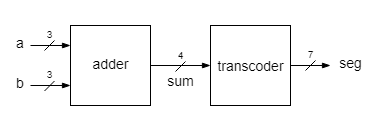
Exercise 2
Implement a 3 bit adder whose result is displayed as a hexadecimal digit.
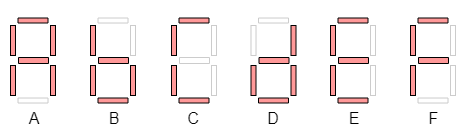
The result of the 3 bit addition is in the range [0, ... ,14] and it may be written in the hexadecimal base using only one digit. The transcoder must be extended to show hexadecimal digits greater than 9. Use the most common 7-segment symbols for them:
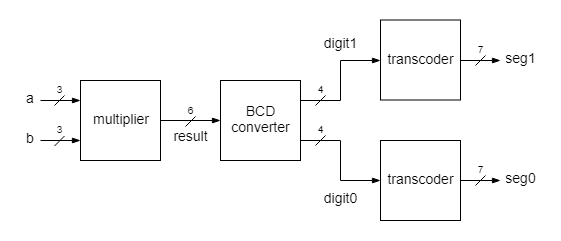
Exercise 3
Implement a 3 x 3 bits multiplier, with the result shown in decimal base as a 2 digits number.
This project comprises a top module with 4 blocks. The first block, multiplier, takes in two 3 bit numbers, a and b, and delivers the result of their multiplication in binary format. The input operands and the result are treated as unsigned integers (natural numbers). The next block, BCD converter, converts the result from the binary format to the decimal. The decimal digits are coded in binary, therefore a multidigit number is coded in the so called BCD format (Binary-coded decimal), where each decimal digit is represented as a 4 bit number.